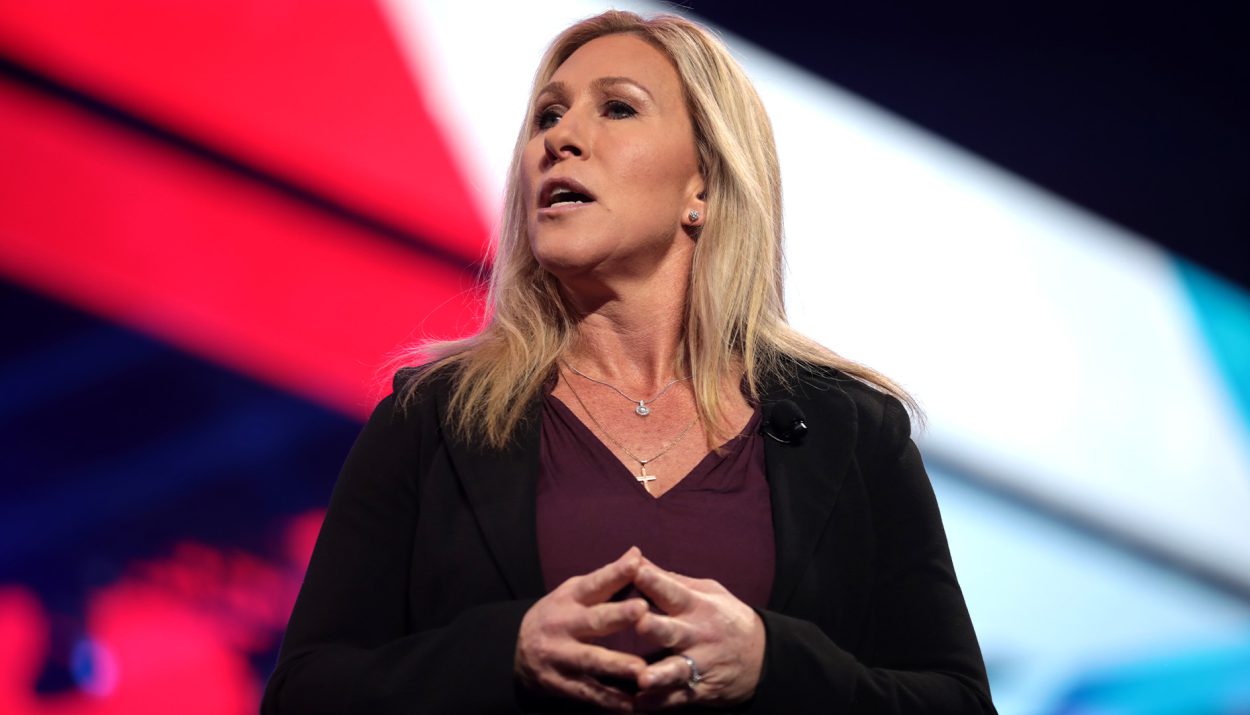
Disinformation and controversy swirled as U.S. Representative Marjorie Taylor Greene proposed an amendment to crucial aid for Ukraine that critics say aligns suspiciously with Russian talking points.
The Georgia Republican’s amendment regarding ethnic Hungarians sparked accusations that she takes direction from Moscow and reignited calls to investigate any illicit Russian ties. Greene’s reputation for inflammatory theatrics precedes her, but this amendment struck experts as uniquely tailored to advance the Kremlin’s narratives about Ukraine.
MTG Proposes Controversial Ukraine Amendment
Marjorie Taylor Greene stunned observers by proposing an amendment to strip funding from Ukraine unless the country lifts restrictions on the Hungarian minority’s language rights.

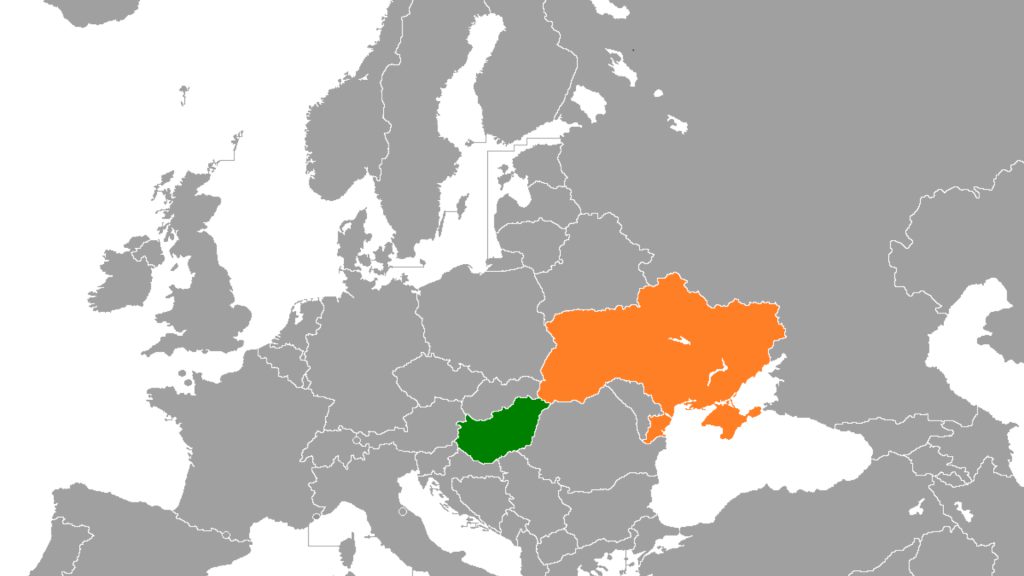
The controversial amendment specifically cites the Hungarian population in Transcarpathia, a region in western Ukraine.
Criticism of Ukraine’s Education Law
Hungarians make up 12.1% of Transcarpathia’s population and have criticized Ukraine’s 2017 education law requiring Ukrainian as the language of instruction in state schools.

Greene’s amendment echoes the complaints of Hungary’s Prime Minister Viktor Orban, who has sought to expand his influence over ethnic Hungarians living outside Hungary’s borders.
Suspicions of Russian Influence
However, others see the hand of Russia behind Greene’s proposal. The narrative that Hungary’s minority is oppressed in Ukraine aligns with Russian disinformation campaigns seeking to undermine Ukraine.

Tom Nichols, a political scientist, noted that Greene’s staff would have had to research obscure details about Transcarpathia to craft the amendment, suggesting Russian assistance.
Greene’s History of Controversial Positions
Greene is no stranger to controversy. She has promoted conspiracy theories about 9/11 and school shootings in the past.

However, openly siding with Russian interests marks a new low and raises questions about her judgement and influences.
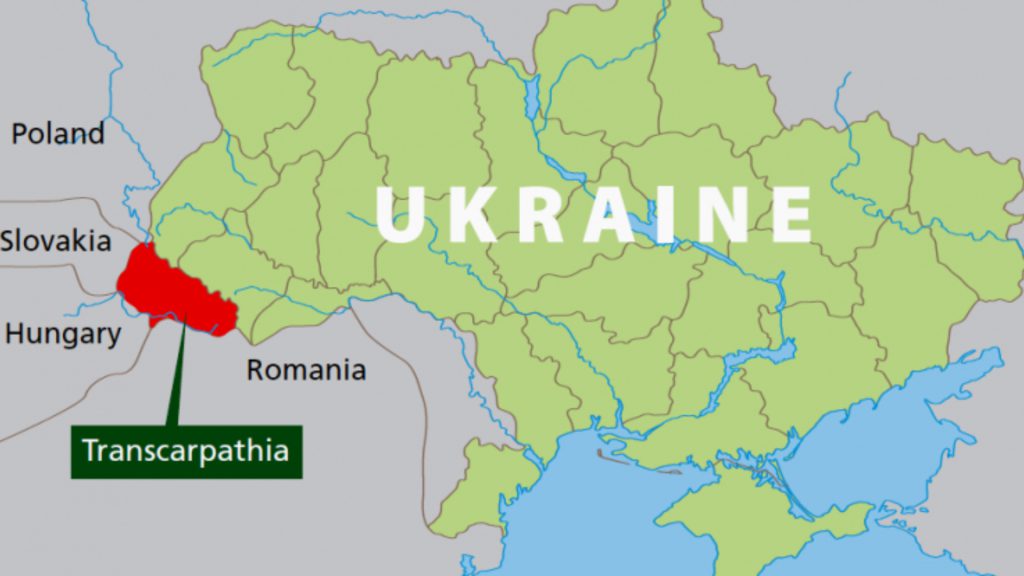
The Transcarpathia Region of Ukraine Explained
The Transcarpathian region, also known as Zakarpattia Oblast, is located in the westernmost part of Ukraine. Bordered by Poland, Slovakia, Hungary, and Romania, Transcarpathia has a diverse population with a complex history.

The Transcarpathian region may be small, but its diverse blend of cultures and complex history give it an importance that belies its size. Managing minority rights and economic challenges will be crucial for Ukraine to maintain control of this strategic borderland. With care and wisdom, Transcarpathia could become an example of how Ukraine values and protects its diversity of identities.
A Melting Pot of Cultures
Transcarpathia is home to over a dozen ethnic groups, including Ukrainians, Hungarians, Romanians, Russians, and Rusyns.

The region was once part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and later Czechoslovakia before becoming part of Soviet Ukraine in 1945. This complex history has left its mark, with many residents speaking multiple languages like Hungarian, Romanian, Rusyn, and Russian in addition to Ukrainian.
A Source of Tension
The large Hungarian minority population has been a source of tension with Ukraine’s nationalist government. In 2017, Ukraine passed an education law making Ukrainian the required language of study in state schools.
Hungary and the Hungarian minority criticized the law, saying it infringed on minority rights. The dispute even led Hungary to block Ukraine’s cooperation with NATO.
An Economic Backwater
Transcarpathia remains one of the poorest regions of Ukraine. Infrastructure and industry were neglected for decades under Soviet rule.
Most residents are employed in low-wage sectors like agriculture, forestry, and tourism. However, the stunning natural scenery, medieval castles, and wine country have the potential for economic growth through tourism.
Hungary’s Territorial Claims in Ukraine
Hungary has long claimed parts of western Ukraine, specifically the Zakarpattia region. This claim is rooted in history, as the area was once part of the former Kingdom of Hungary.

However, after World War I and the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the region became part of Czechoslovakia. Following WWII, the Soviet Union annexed Transcarpathia and made it part of Soviet Ukraine.
Hope To Regain Control Even After Independence
When Ukraine gained independence in 1991, Hungary still hoped to regain the territory. Relations between the two countries were strained for years over the issue of ethnic Hungarians living in Ukraine.

Hungary’s nationalist prime minister, Viktor Orban, has repeatedly stated his belief that ethnic Hungarians living outside the country’s borders deserve special rights and protection. Orban likely sees territorial claims in Ukraine as a way to bolster his popularity at home.
Restrictions on Minority Languages in Ukraine
The notion that ethnic minorities in Ukraine face persecution is a controversial one pushed by Russian disinformation campaigns.
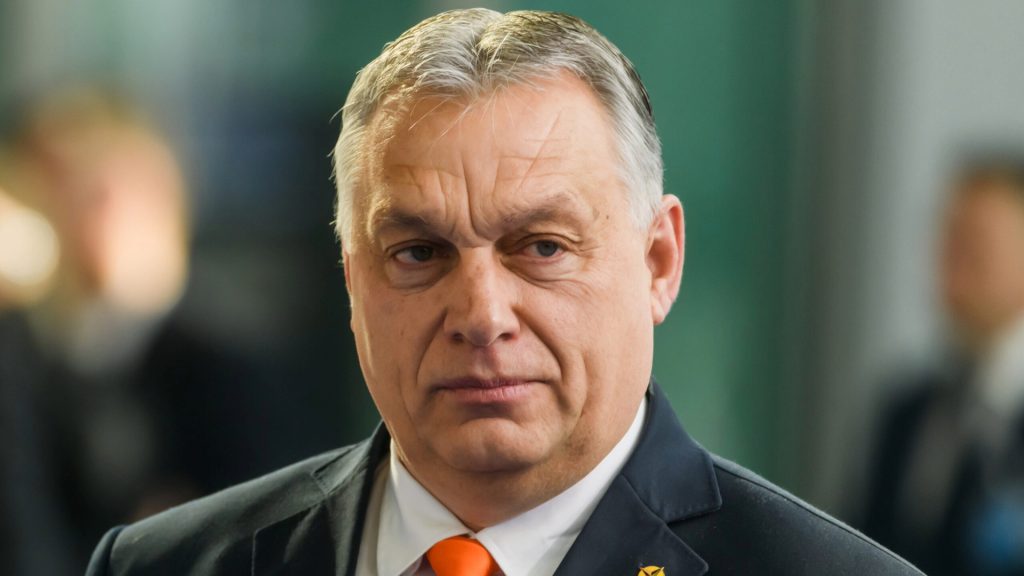

Hungary’s leader Viktor Orban, who was promised Ukrainian territory by Putin, and Russian propaganda have spread the idea that Hungarians living in western Ukraine’s Transcarpathia region are oppressed.
Responses Accuse MTG of Pushing Russian Disinformation
Marjorie Taylor Greene’s proposed amendment regarding ethnic minorities in Ukraine was met with harsh criticism from experts and political commentators.
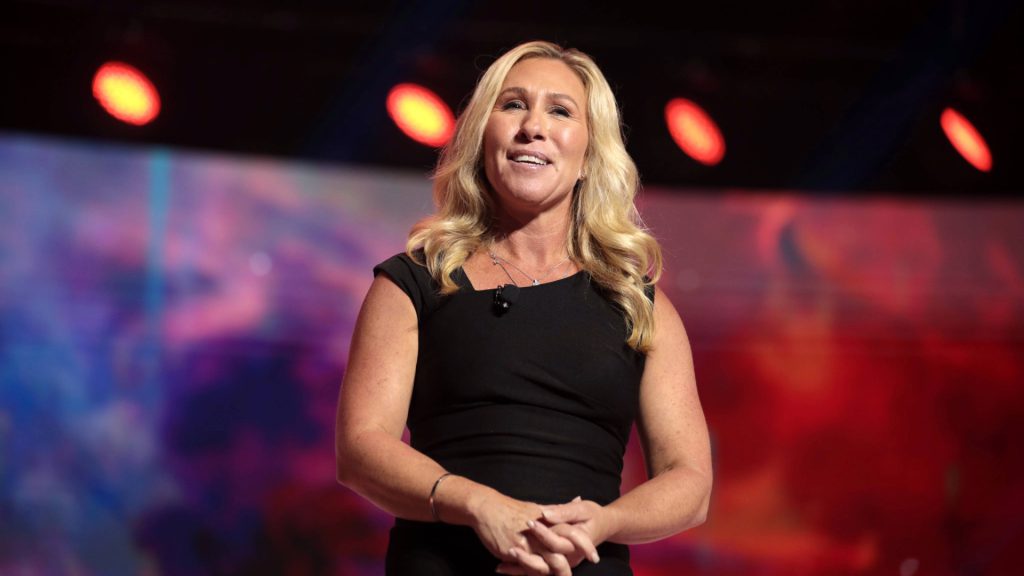

Many accused the congresswoman of parroting Russian propaganda and disinformation in an effort to undermine U.S. support for Ukraine. While Greene denies allegations of Russian influence, her pattern of echoing pro-Russia talking points and stances continues to raise eyebrows.
Pattern of Pro-Russia Behavior
For some, Greene’s amendment fits into a larger pattern of pro-Russia behavior. Since taking office, Greene has voiced support for Putin, spread misinformation about Ukraine favored by Russian state media, and opposed sanctions on Russia and military aid for Ukraine.
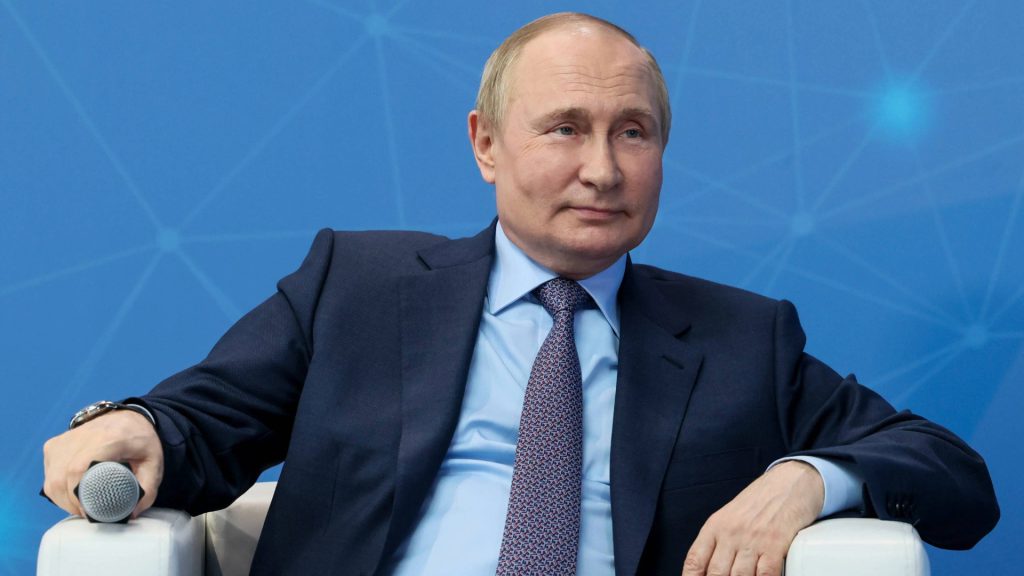

Her amendment, experts argue, aligns conveniently with key Russian foreign policy goals like undermining Western support for Ukraine.
Implications for US Support of Ukraine
Ukraine relies heavily on funding from the US and Western allies as it continues to battle Russian-backed separatists in the Donbass region. Over 13,000 lives have been lost in the conflict so far.

Any reduction or elimination of US monetary support could severely hamper Ukraine’s ability to defend itself and maintain its sovereignty in the face of Russian aggression.